When planning heating systems, various wiring methods are used, one of which is a bypass. What is a bypass in a heating system, every specialist in the development and installation of domestic heating systems knows, the information can be useful to the owner of a cottage or summer house if he is engaged in arranging the heating of his home with his own hands.
Although the bypass is the simplest detail, it cannot be dispensed with in multi-apartment high-rise buildings with economical single-pipe wiring, the use of the element is also widely practiced in domestic heating networks. When arranging heating, the correct placement of the bypass in the right places allows you to achieve high efficiency of heating the room, save financial resources, and avoid the negative consequences of emergencies that arise during the operation of the equipment.
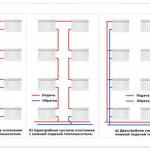
Fig. 1 One-pipe and two-pipe connections
What is a bypass in a heating system
Bypass - the Russian-language pronunciation of the English word “bypass”, translated means bypass, bypass, bypass, detour. The device plays a similar role in the pipeline system - it creates a bypass path for the working fluid, becoming a kind of bypass bridge between the entry and exit points of the included heat exchange devices.
Structurally, the part is a short piece of pipe made of a material similar to the pipes, installed at a short distance from the inlet and outlet fittings of the connected heat exchanger. The pipe section can be welded in the case of using metal pipes, fixed to threaded fittings when using metal-plastic, soldered into the polypropylene line.
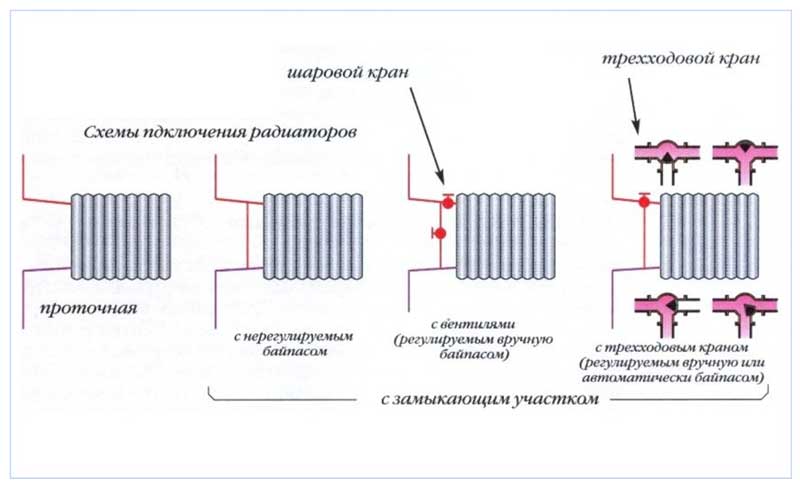
Fig. 2 Radiator connection diagrams
Photos of finished structures
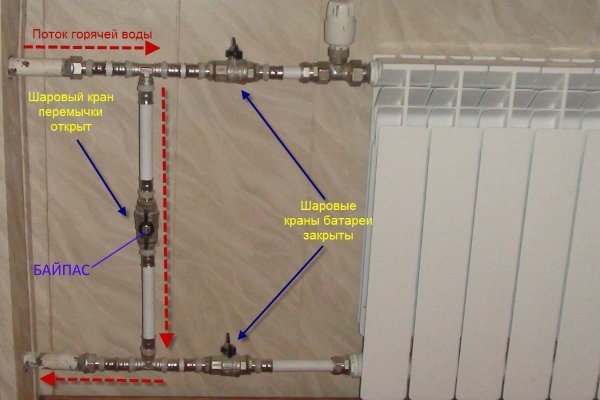

Photo 1. A bypass in the form of a jumper connecting the supply and return. Ball valves are also used in the design.
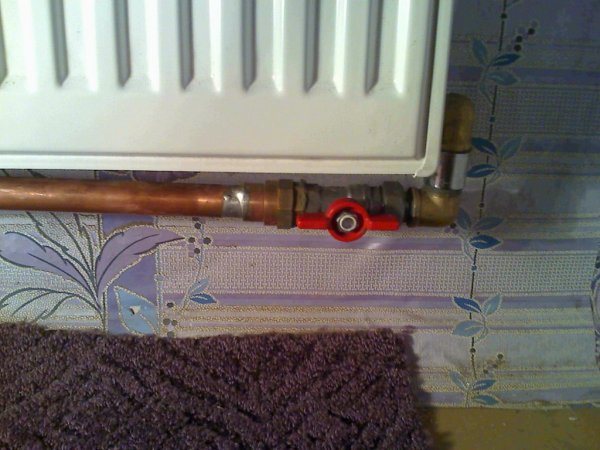


Photo 2. Bypass installed on the pipe of the heating system. The design uses a ball valve.
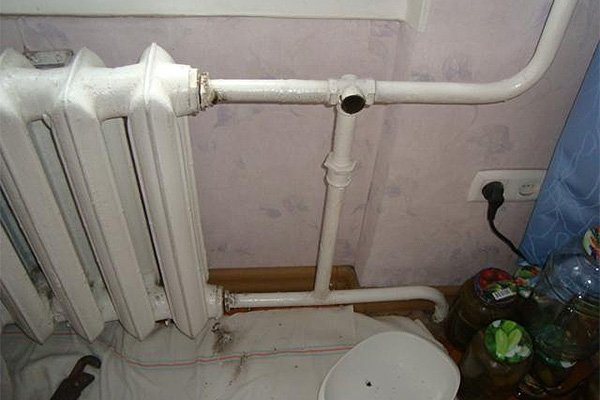


Photo 3. A bypass in the form of a jumper installed on a cast-iron heating radiator. Design without valves and taps.
Why do you need a bypass in the heating system
To understand what a bypass is for, and to appreciate the importance of installing this element, you should consider the main types of wiring for household heating systems.
When installing household heating systems, a sequential (one-pipe) and parallel (two-pipe, collector) supply of a working fluid to heat exchange units is distinguished, in the first case, the coolant passes sequentially through all devices, gradually cooling at the end. With a sequential scheme, the coolant is supplied to the heat exchangers from the highest point or from the bottom, while it circulates in a closed ring, returning to the boiler through the return pipes.
A single-pipe system requires less materials for placement and is widely used in multi-apartment housing; during installation, to avoid the main drawback - weak heating of the most distant radiator in the network, inserting a bypass jumper helps. The purpose of the bypass is to create an additional path bypassing all radiators, providing a coolant supply of the same temperature to each of them, this contributes to a more uniform heating.
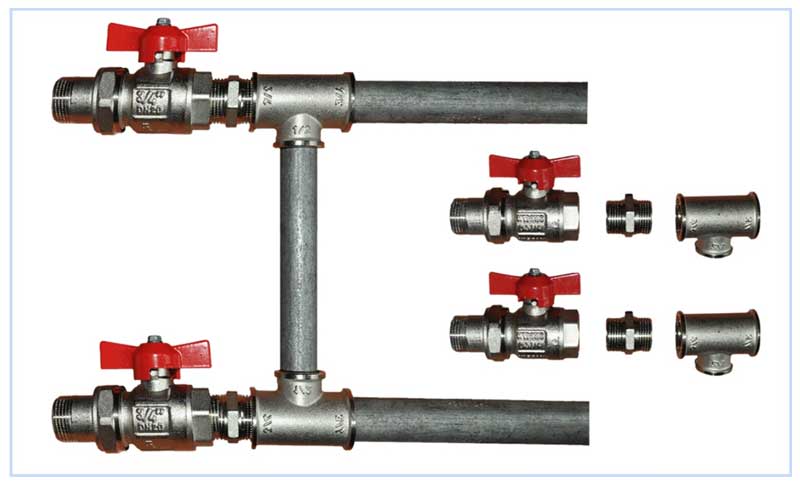

Fig. 3 Structural metal bypass device and its connection
The second important function of the installed bypass branch pipe is to ensure uninterrupted delivery of the coolant to all radiators in the event of a breakdown or disconnection of one of them in the serial circuit.From the diagram in Fig. 1, it is clear that in the absence of a bypass between the pipes, if one of the radiators fails (leakage, blockage), the delivery of the coolant to the subsequent circuits stops, as a result of which the residents are left without heat, and the entire system is threatened by freezing.
The third purpose of the bypass is to maintain a constant circulation of the coolant in the event of a breakdown of the compression pump of the heating system. In the case of a bypass, the system works in a natural way, providing circulation bypassing the pumping line - this guarantees uninterrupted heating of the premises in the dwelling. It should be noted that in order to ensure the mode of natural circulation when the pump is turned off, an appropriate design is necessary (large pipe diameter, slopes); if these conditions are not met, the circular movement of the liquid due to thermal expansion should not work.
An important advantage of the bypass is the ability to turn off any radiator for its repair, preventive maintenance or replacement. This is achieved due to the location of two ball valves on the radiator inlet and outlet fittings, after they are locked, the radiator can be easily removed for repair, maintenance, and building up additional sections. The bypass performs similar functions when installed in parallel in the circuit of the compression electric pump - with the help of two ball valves, the electric pump is easily disconnected from the heating network for repair, maintenance, replacement of equipment without draining water and stopping heating of the premises.
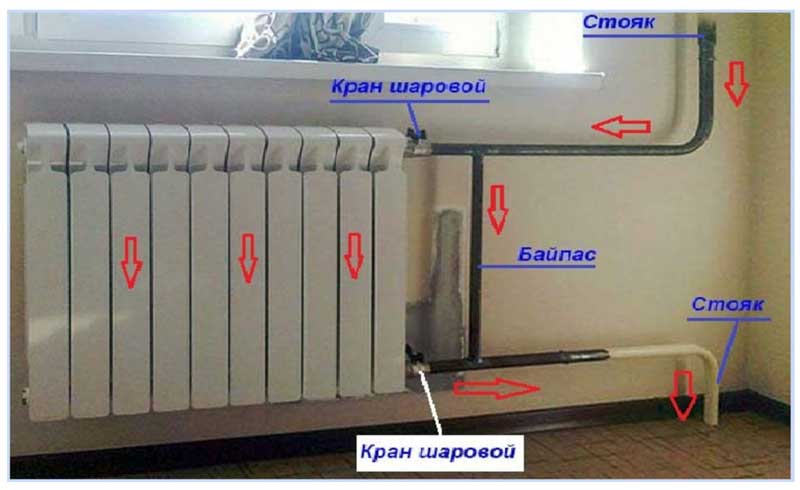


Fig. 4 The principle of operation of the bypass in the heating radiator circuit
Bypass in the boiler room
In boiler piping schemes, a bypass line is also necessary in 2 cases:
- as a bypass for a circulation pump;
- for organizing a small circulation loop for a solid fuel boiler.
A pump installed on a bypass pipe is found in heating systems quite often, sometimes even without special need. The fact is that a one-pipe or two-pipe heating system, originally conceived with forced circulation, will never be able to function when the pump is turned off.
Hence the conclusion: when connecting a system designed for forced circulation to the boiler, there is no need to put the pump on the bypass. Switching off and removing the unit in any case will stop the movement of the coolant, so the pump is installed in a straight line.
While the pump is running, it presses the valve from the reverse side with its pressure and does not let the flow in a straight line. One has only to turn off the electricity or turn off one of the taps, as the pressure disappears and the bypass valve opens a direct path to the coolant, and the convective movement of water is restored. You can safely remove the pump or clean the sump, the system will not be affected by this, it will simply switch to another mode.
The principle of operation is simple: the valve does not let cold water from the system into the boiler until the coolant circulating through the bypass line heats up to the required temperature. Then the valve opens and passes cold water into the circuit, mixing it with hot water. Then condensation does not form on the walls of the furnace and corrosion does not occur.
Sometimes you also need a bypass in the water supply system. For example, to remove a heated towel rail in the bathroom for repair, flushing or replacement. Since it is connected to a hot water supply riser, then dismantling it in an apartment building will create a lot of inconvenience. It is easier to foresee this in advance and put a jumper with a tap when installing the heater.
In the classic version of the one-pipe system, the bypass is mounted next to the radiators. When used for heating solid fuel boilers, the bypass jumper is more often used for the entire heating system of the house.
- a check valve, pumping equipment and filter system are being installed;
- assembly of the assembly into the main pipeline is carried out using couplings;
- an additional valve is installed on the jumper, which allows, if necessary, to shut off the circulation of the liquid.


Installation on the return pipe of the heating system
Installing a bypass is not considered time-consuming if you carefully study the work and the nuances of installation. With the correct selection of components, the heating system will be more energy efficient and reliable.
- as a bypass for a circulation pump;
- for organizing a small circulation loop for a solid fuel boiler.
A pump installed on a bypass pipe is found in heating systems quite often, sometimes even without special need. The fact is that a one-pipe or two-pipe heating system, originally conceived with forced circulation, will never be able to function when the pump is turned off.
While the pump is running, it presses the valve from the reverse side with its pressure and does not let the flow in a straight line. One has only to turn off the electricity or turn off one of the taps, as the pressure disappears and the bypass valve opens a direct path to the coolant, and the convective movement of water is restored. You can safely remove the pump or clean the sump, the system will not be affected by this, it will simply switch to another mode.
The principle of operation is simple: the valve does not let cold water from the system into the boiler until the coolant circulating through the bypass line heats up to the required temperature. Then the valve opens and passes cold water into the circuit, mixing it with hot water. Then condensation does not form on the walls of the furnace and corrosion does not occur.
Sometimes you also need a bypass in the water supply system. For example, to remove a heated towel rail in the bathroom for repair, flushing or replacement. Since it is connected to a hot water supply riser, then dismantling it in an apartment building will create a lot of inconvenience. It is easier to foresee this in advance and put a jumper with a tap when installing the heater.
It is recommended to install a bypass if the natural heating circulation is insufficient. This is done in case of unsuccessful or incorrect installation of the system. In this case, the design includes a jumper device made of a piece of pipe connecting the radiator supply pipe to the return pipe.
At the stage of installing this device into the system, it is worth adhering to some requirements. Thus, the diameter of the pipe of the device must be matched to the size of the smaller diameter of the supply and return pipes. In this case, the laws of hydraulics will produce water through the least resistance, while bypassing the radiators.
The device can be assembled independently, but it is better to purchase it ready-made. To ensure automatic temperature control in the home, a thermostat serves as an alternative to ball valves. More accurate circulation of warm water from the system is achieved due to the fact that in the middle of the regulator in question there is an adjusting ball valve.
Listening to the advice of experienced professionals, researching the information of interest on your own, it becomes possible to have a reliable and high-quality installation of a heating system for your home.
What are the types of bypasses
Although the bypass is a fairly simple element, the range of its functions can be significantly expanded through the use of various types of sanitary fittings built into it. The design of the bypass depends on the line in which it is used, the type of residential or industrial buildings with installed single-pipe heating.
Fixed bypass
The simplest bypass design is an unregulated bypass pipe that connects the pipelines between the inlet and outlet lines.Such an element is usually installed in apartment buildings, where the absence of a shut-off device prevents accidental overlap or partial blocking of the bypass and, accordingly, disruption of the entire system, its imbalance.
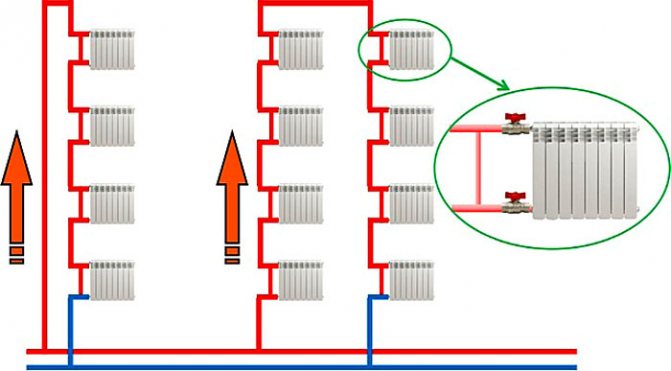
The unregulated unit is widely used in the widespread "Leningrad" - a one-pipe line with a large-diameter straight bypass pipe and a chain of heating batteries connected in parallel to it.


Fig. 5 "Leningradka" - a popular piping scheme for a one-pipe structure
Manually controlled bypass
Since a part of the coolant passes through the bypass, installed in parallel to the connected heat exchange devices, bypassing the heating devices, to increase the supply of the medium to the radiator, its cross section is made smaller than other pipes, increasing the hydraulic resistance. Typically, the diameter of the bypass in a one-pipe heating system is less than the pipes that fit from the central riser to the radiator by a quarter of an inch, which in turn have an outer dimension smaller than the riser pipes by the same amount.
It is clear that this system is unregulated and does not allow effective use of the system - the radiator with a large number of sections does not always fully warm up due to the escape of the coolant through the bypass pipe.
Varieties of bypasses
There are several types of bypasses for use in heating systems.
Unregulated
Performed in the form of a bypass jumper... There is no shut-off and control valves (tap or non-return valve) on the lintel.
Operating principle
- Part of the hot HP that has passed through the bypass is mixed with the flow at the outlet of the battery and increases the temperature of the heat pumpentering the next battery.
- If the heater fails, the heat pump bypasses the battery, keeping circulation.
Features of the
- With vertical wiring the diameter of the bypass is one step less than the diameter of the supply pipes.
- With horizontal routing the bypass in diameter coincides with the supply pipe, and the diameter of the branches up the battery is a step smaller (the heated HP tends upward).
- Install as close to the battery as possible (next to the shut-off valves).
Manually operated: what it is


For manual regulation of the heat pump flow through the bypass, it is equipped with or ball valve for overlap, or a three-way valve at the intersection of the bypass and the supply pipe to the radiator.
Operating principle
The three-way valve has three positions:
- closes the bypass and directs the entire HP flow to the radiator;
- closes the supply to the radiator and opens the bypass for the HP flow (position for repair or replacement of the radiator);
- opens both paths for the TN: to the battery and along the bypass.
Features of the
- Bypass valve next to the battery they are usually installed in order to close the jumper with a poorly heating radiator. But such a solution is technically illiterate - the flow through the bypass is approximately equal to the flow through one section of the radiator, so a significant increase in the temperature of the battery will not occur.
- In a private house, a ball valve installed in parallel with the central pump on the return pipe. The valve is closed when the pump is running, and opens manually when the pump fails or when it is replaced to restore circulation.
Attention! In an apartment building with a one-pipe system, a crane on a radiator bypass it is forbidden to install... It can lead to a violation of circulation and a lowered temperature of the coolant entering the neighboring apartments.
Automatic how it works with a pump
Installed parallel to the CN... A check valve is mounted on the shunt pipe to automatically restore circulation through the bypass when the central pump stops.
Operating principle

Bypass with differential (ball) valve installed in parallel with the CN on the vertical pipe for supplying the coolant from the boiler.
When the pump is running, part of the flow presses the rubber ball against the funnel and closes the HT passage through the shunt pipeline.
When the pump is turned off, the ball rises under the pressure of the HP flow through the supply pipe and opens the passage for the HP through the bypass.
Lobe check valve bypass installed parallel to the pump on a horizontal return pipe (in a gravitational system). The shutter (petal) of the valve is pressed against the seal by the flow from the pump, closing the bypass. When the pump stops, the petal moves away from the seal (opens) under the action of the hydraulic return pressure, restoring circulation.
Important! Required periodically check the function of the check valveso that it does not become clogged with deposits and dirt.
The check valve is usually mounted on the main pipe (supply or return). Bends from the main pipe to the central pump make two sizes smaller in diameter.
Bypass in the heating radiator piping
When installing the jumper assembly, the following basic rules are observed:
- The jumper is placed as close as possible to the inlet radiator fittings - this contributes to more efficient heating of the heat exchangers as a result of the passage of large volumes of the coolant through them.
- At the inlet and outlet of the batteries, it is necessary to place shut-off ball valves, which allow them to be disconnected from the network for preventive and repair work without draining the coolant and stopping heating.
- When using pipelines made of modern materials - metal-plastic or polypropylene for heating individual residential buildings, it is better to install a control valve in the bypass bypass. With its help, it is possible to reduce the flow passing through the jumper, and also to adjust the heating temperature of all radiators in the line by changing the cross-section of its passage channel.

Fig. 8 Examples of installation of a control valve between bypass
What is a bypass on the radiator for?
As noted earlier, the use of a bypass with heating radiators is effective only in one-pipe circuits, the part allows you to achieve a more uniform heating of all heat exchange units. Also, the presence of a bypass allows water to be supplied to subsequent heat exchange devices in the event of failure or shutdown of one of them.
With the help of a jumper installed, the system can be manually adjusted so that all radiators are evenly heated. For this, the cross-section of the bypass bypass to the heat exchangers closest to the boiler is increased, and at the most distant radiators, it is reduced, thus controlling the flow passing through the batteries.
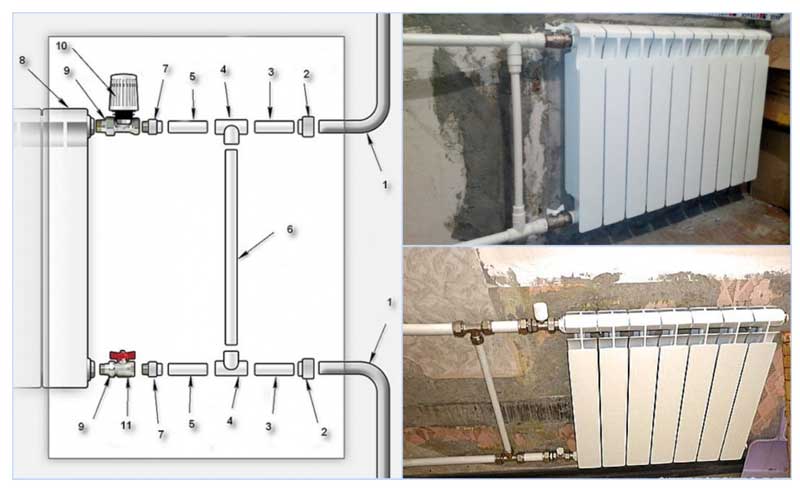

Fig. 9 Radiator piping with polypropylene and metal-plastic pipes
Self-assembly of the bypass in the radiator piping
Before installing the bypass, you can consider factory samples - the industry produces finished products for radiator heat exchangers, in which the distance between the connecting inlet fittings corresponds to the standard axial dimension from the upper and lower radiator connection points.
The problem of how to make a bypass to the heating system has different solutions depending on the material of the pipes used. Usually, self-installation of this element does not cause any particular difficulties for any owner (with the exception of polypropylene pipes) who has minimal plumbing skills and the necessary tools (one or two adjustable wrenches are needed).
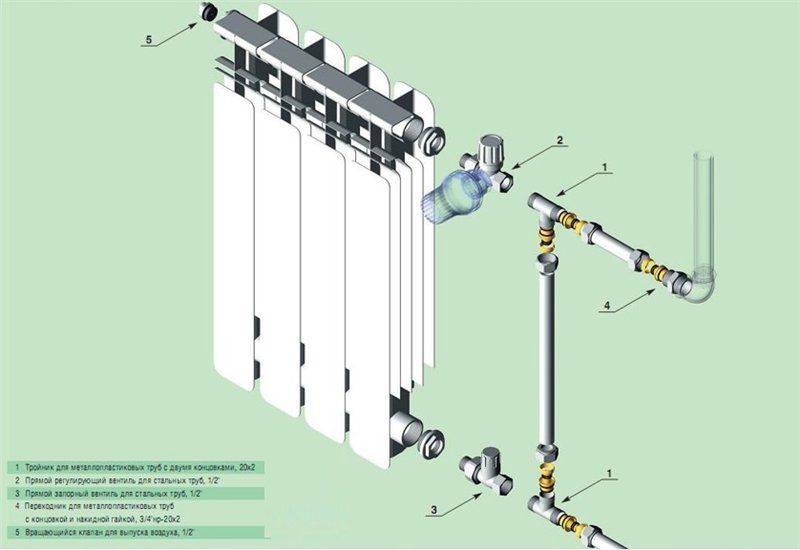
Fig. 8 shows the installation of a bypass in a water supply line made of polypropylene, which is connected to the riser 1 through transition couplings 2. Bypass 6 is connected through a tee 4, connected to the main by pipe sections 3 and 5.To the thermostat 10, connected to the radiator 8 by means of an American 9, a pipe segment made of polypropylene is connected using a fitting adapter from metal to polypropylene 7, in a similar way the line is connected to the shut-off valve 11.
In this scheme, all pipes have the same outer size, therefore, the operation of such a structure is ineffective (the internal channel section of the bypass branch pipe in a single-pipe supply must be smaller), for its normal operation it is necessary to insert a control valve into section 6, which reduces the channel passage opening.
In a similar way, a bypass jumper is mounted on the battery when using metal-plastic, the structure can be assembled most quickly using compression fittings (Fig. 8).
It should be noted that in the circuit in Fig. 8 pipe sections 5 are optional, the tee can be connected directly to the ball valve and thermostat by extending section 3.
If metal pipes are used in heating for water supply, a bypass jumper can be placed directly near the taps on the inlet and outlet battery fittings by connecting two tees to them. It is not difficult to make the diameter of the bypass lintel smaller than the main line with a small cross-sectional cross-section pipe; in this case, it is not necessary to put the shut-off valve in the lintel.
Installing a bypass - conditions and methods
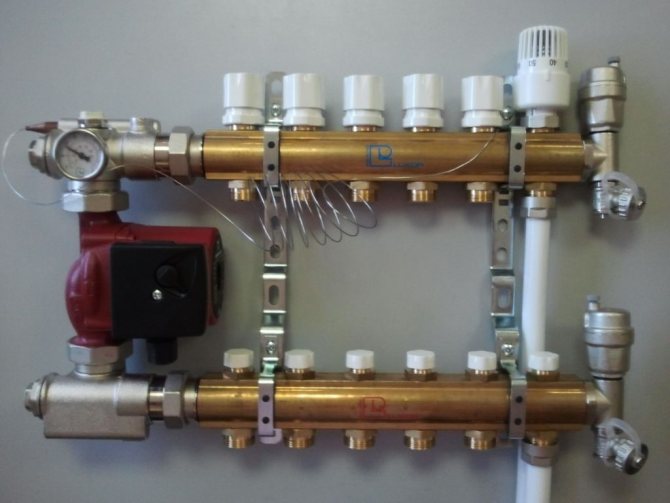
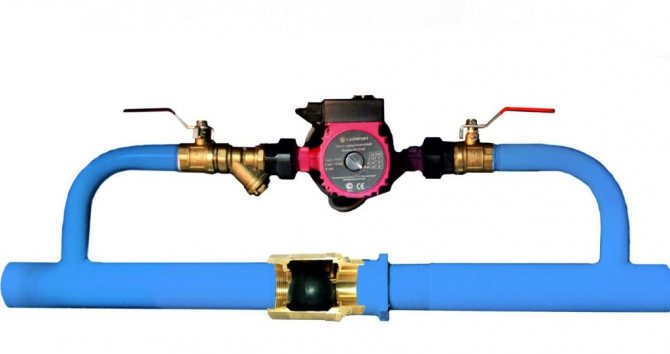
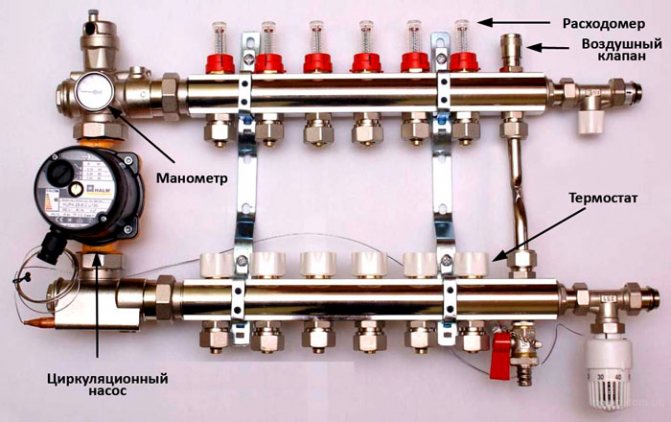
Bypass for circulation pump with ball valve
Why do you need a bypass in the heating system in the area where the electric pump is installed? It would be more accurate to say that the pump is installed directly on it. This is practiced when an electric supercharger is placed in the gravity circuit, the one in which the circulation is carried out by gravity. It increases the flow rate and thus increases the efficiency of the circuit. This is due to the fact that at a higher speed the coolant reaches the extreme radiator with less heat loss.
There are two options for installing a bypass for a circulation pump:
- on a new circuit;
- on an existing contour.
There is no difference in installation. What you need to pay attention to is the presence of shut-off valves on the central line between the bypass pipes. This is necessary in order for the coolant to pass through the bypass for the circulation pump, and also so that a reverse flow is not created.
It is imperative to install a ball valve, and not a check valve, as some plumbers do.
To understand why, let's take a step-by-step look at how it works:
- when the pump is running, it accelerates the coolant;
- water from the bypass enters the line and begins to move in both directions;
- in one direction (the right one), it leaves without hindrance, and in the second side it bumps into a check valve;
- the valve closes and thus prevents circulation in both directions.
That is, the water after the pump presses on the valve disc more strongly than before it, since the speed of the coolant behind the pump will be higher. As planned, when the pump is turned off, the coolant stops pressing on the check valve and does not block it. This allows water to circulate by gravity through the main line, without entering the bypass.In practice, the bypass for heating with a check valve does not work as expected.
The fact is that the check valve disc creates a strong hydraulic resistance equal to one meter. In the gravitational circuit, the coolant simply cannot withstand such valve resistance and the circulation will stop.
Therefore, before installing a bypass in a heating system with a check valve, you need to understand that, in fact, installing a pump on the bypass will not make any sense. With such success, it could be installed directly on the highway, while deliberately abandoning the possibility of using the heating circuit autonomously.Do you need a bypass in the heating system in this case? It turns out that, no.
If, instead of a check valve, you put an ordinary ball valve, then you yourself will be able to control the vector of water circulation along the contour. Let's take a look at how to make a bypass to the heating system, on which the pump will be installed. In such a scheme, it consists of separate elements:
- threaded nozzles that are welded into the line;
- ball valves - installed on both sides;
- corners;
- coarse filter - placed in front of the pump;
- two American women, thanks to which the pump can be removed for inspection or repair.
If you are doing a bypass in a heating system with your own hands, it is important to observe the correct location of the pump on it. The impeller shaft must be horizontal with the terminal box cover facing up. If, when properly installed, the terminal box cover faces downward, its position can be changed by removing the four screws on the housing.
To install the bypass pipe in the heating system of polypropylene pipes correctly, follow these guidelines:
- The diameter of the bypass pipe is taken to be smaller than the diameter of the pipeline;
- The lintel should be located as far from the main riser as possible and as close to the serviced device as possible;
- The bypass is mounted horizontally to avoid air pockets;
- Install the bypass pipe section only after draining the coolant.
The first way to mount a jumper for a radiator is welded. The inclusion of polypropylene in the heating system ensures maximum reliability of the circuit, but steel pipes can also be used, albeit with less efficiency. PVC or metal pipes for the bypass are drilled in the right place, a lintel pipe is inserted into the hole, the joint is scalded.
The second method is clutch. The radiator is also dismantled, the jumper is fixed in place using factory couplings, shut-off valves are cut into the edges of the bypass. In the same way, the radiator is attached and connected to the circuit in a new place.
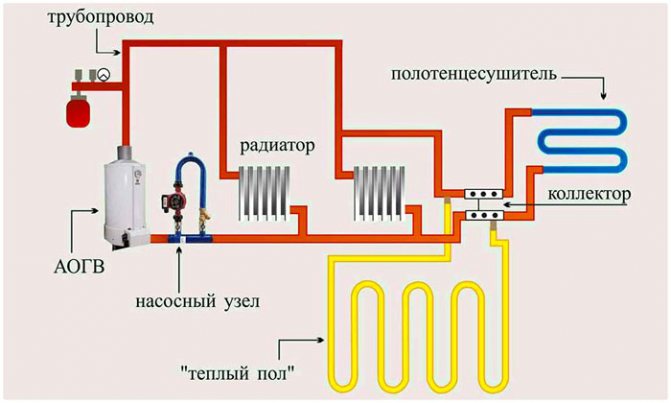
It is necessary to tell in more detail how to correctly install the bypass in the "warm floor" scheme, since the temperature of the coolant with such a solution should not be more than 45 ° C. Installation of underfloor heating provides for the installation of a collector, and the bypass jumper on it acts as a bypass section of the heating route and a mixing unit.
The mixing unit in the manifold is a three-way valve with a temperature sensor. The valve divides the coolant flow into two parts, one of which it directs into the pipes of the "warm floor" device, and the second through a parallel line. In this case, the supply and return are mixed, after which the working fluid flows back to the boiler jacket.
Read more: Radiation heating system of a private house - advantages and disadvantages
Before making a bypass along a small circuit, you need to understand that a jumper through the three-way valve will connect the supply and return, that is, the collector must be included in the underfloor heating circuit. The bypass works in such a scheme as follows: after starting the boiler, the three-way one blocks the flow of cold working fluid from the heating main to the heat generator.
After the coolant heats up to the set temperature (45-50 ° C), the automatic valve will open and let a certain amount of hot coolant into the return pipe. This technique avoids the accumulation of condensate in the combustion chamber and on the surface of the boiler jacket.
A metal or PVC section of a bypass pipe is necessary in any heating scheme, since its use is an economical option for distributing heat with high efficiency while saving solid, gas, liquid or electrical energy.Simply put, the volume of the coolant that is supplied to radiators and other devices and devices is reduced when the bypass is installed, without violating the norms for calculating heat transfer from both individual elements of the system and the entire structure.
As a rule, it is necessary to embed a circulation pump into the heating system together with the bypass section of the pipe. The installation of bypasses can be done by hand. The circulation pump must be installed in just such an area. In this case, the bypass will consist of the following interconnected parts: a filter, a pumping device, a shut-off valve, which can be replaced by an automatic valve.
In this case, the entire system must be installed in the pipeline near the area connected to the boiler. This requires the installation of a shut-off valve in the section from the entrance to the exit of the bypass path.
Consider the principles of operation of a heating system with a circulation pump and a bypass. When the circulation pump is turned on, the valve located on the bypass pipe must be opened, since during this period the liquid moves just along the bypass path. This requires the closure of the ball valve, which is located on the main pipeline.
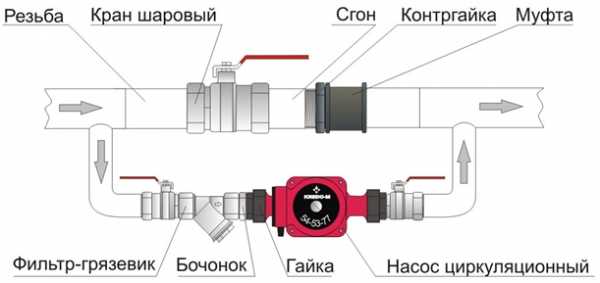

Similar actions are performed in the event of a power outage, since in this case the operation of the circulation pump stops. Shut-off valves will allow water to be directed towards the return. It should be noted that the bypass system may have a check valve, in this case it is enough to do with opening the tap on the return line.
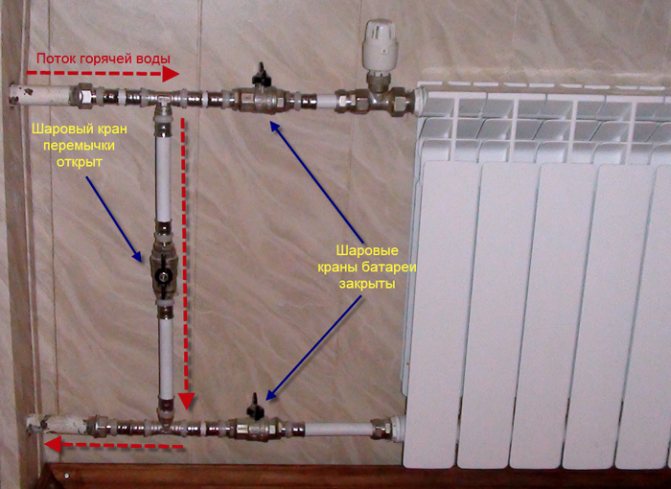

The nuances of installing a regulating device are shown in the diagram
In a one-pipe design, the installation of a bypass for heating is necessary so that when the heating device is replaced, the liquid continues to circulate. In a vertical installation, the radiator is connected to the riser with pipes. The regulator combines the pipes and is mounted in front of the battery.
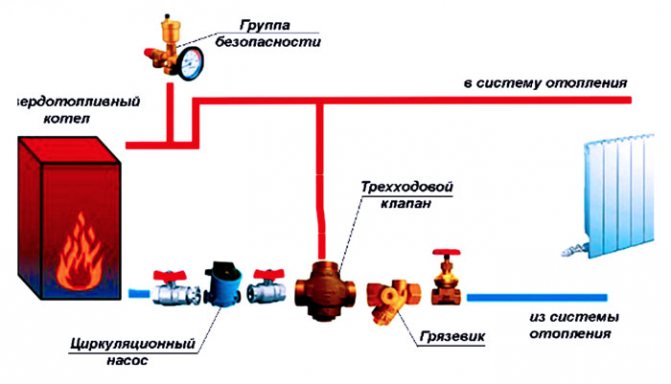

The diagram shows the installation location of the bypass jumper on the entire heating system when using a solid fuel boiler
- creation of constant movement along the main contour;
- regulation of the temperature and flow rate of the coolant directly in the radiator.
Installation of a bypass allows mixing the coolant from the central line with the return line of the battery. This increases the temperature and heating efficiency in general.
The nuances of strapping
- in order to direct the water in the right direction, it is necessary that the cross-section of the lintel be smaller than the cross-section of the main pipeline;
- installation of the structure is carried out next to the heating device, but as far as possible from the riser;
- taps are mounted between the battery inlet / outlet and the regulating jumper;
- thermostats are used to automate the temperature of the device;
- when installing the structure next to the boiler, overheating must not be allowed;
- tees are mounted on the sections of the line;
- do not install a valve or valve on a valveless device.
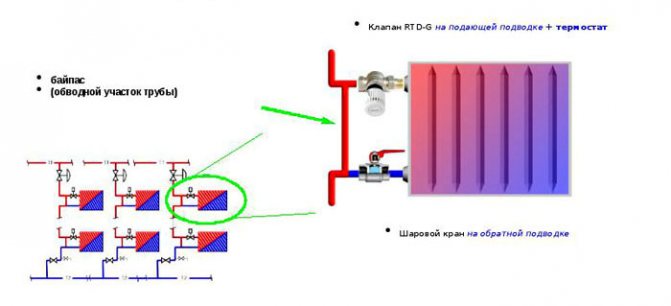

One-pipe piping option
When installing the unit, the building codes must be observed. There must be fasteners or special pipe supports near the bypass device.
Bypass in the circulation pump unit
In modern heating, circulating electric pumps are gradually replacing wiring with natural circulation due to their advantages: the rapid movement of the fluid flow and the regulation of the speed of its movement, which allows for accelerated heating of a cold room. An important advantage is the ability to program the operating modes, the safety of a closed loop when using poisonous antifreeze antifreeze - ethylene glycol.
The only drawback is the dependence on the circulation pump - if there is no power supply or a breakdown occurs, the heat supply becomes impossible.The use of a simple jumper between the sections of the forward and reverse branches with an installed electric pump allows you to get rid of this problem, creating a bypass path for the working fluid. When connecting, it is better to install the element horizontally, although in practice you can also find a vertical arrangement of the bypass.
Sometimes a shut-off valve is cut into the bypass branch pipe, while the other two taps are mounted at the inlet and outlet of the unit with a circular pump - this makes it easy to dismantle the pumping equipment without draining water for repair, maintenance, replacement.
Appointment
The bypass serves the following purposes:
- As a backup line, a backup path in case of an unexpected shutdown of work in the heating system, arising from:
- malfunctions of devices, for example, a circulation pump;
- emergency failures in the system;
- the need to carry out unscheduled repairs of parts or their urgent replacement;
- To quickly drain water and fill the heating device with it;
- Regulation of the intensity of hot water circulation, high-quality heat transfer, device throughput;
- Measurement of liquid volumes;
- Performing the functions of a standard radiator;
- Reducing electricity consumption for heating.
The volume of the coolant entering the battery is reduced in comparison with the flow system by 25-35%. As a result, the heat transfer from the radiator is reduced by about 10%.
Its biggest advantage is that all of the above does not require stopping the main technological process - heating.
It is interesting! American woman for polypropylene pipes: concept and application, overview of couplings, types and sizes of connections
Where else is the bypass used in heating
The answer to the question, what is the bypass in the heating system for, cannot be complete without considering other options for its placement. Many people encounter a similar device every day, using a heated towel rail connected parallel to the central riser. We will consider other areas of use of the bypass pipe below.
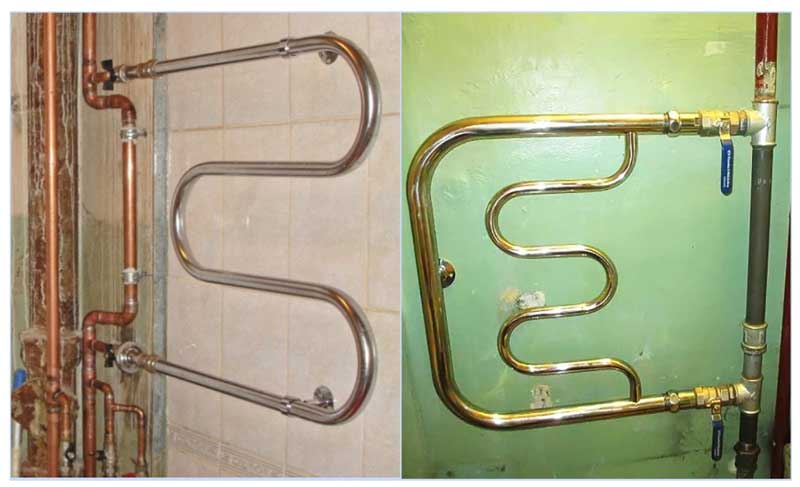


Fig. 11 Heated towel rail - connection options
Bypass in the underfloor heating circuit
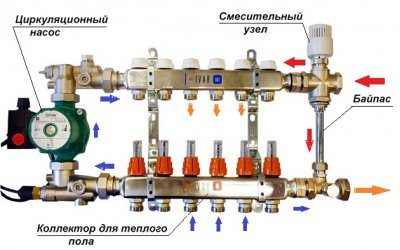
In the presence of a large number of warm water floors in a private house, their connection is carried out according to a collector circuit - this ensures the same pressure and water temperature in each circuit.
Unlike an in-house heating system, the heating of the heat carrier of a warm floor should not exceed 45 degrees - this is due to the convenience of using the floors (too hot a floor surface is impractical and harmful to health) and the extreme temperature characteristics of heat transfer pipes.
The fact is that polyethylene of increased temperature resistance PE-RT, which is an excellent option when used as a pipeline for a warm floor, has a maximum temperature threshold of + 70 C., therefore, liquid with higher temperature values should not be supplied to it.
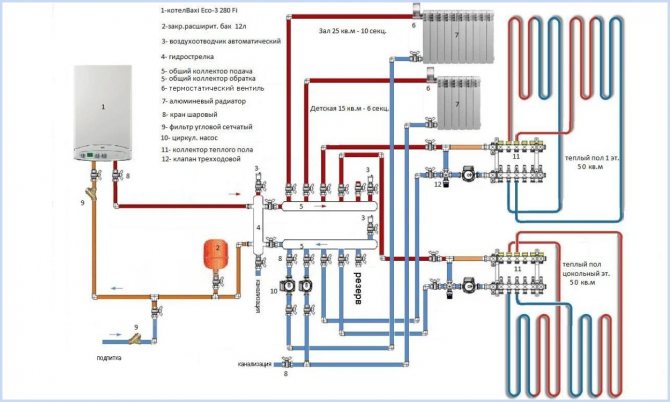

Fig. 12 Multi-circuit collector circuit for heating a cottage
The bypass connecting the supply line located at the bottom of the collector group (determined by the presence of flow meters) and the upper return line (on its collector there are control valves with removable caps for screwing the servos) feeds cooled water from the return line to the direct collector inlet. Thus, through the mixing unit in the form of a tee, a decrease in the total temperature of the incoming liquid is achieved by mixing in a cold water flow to it.
On sale there are ready-made manifold mixing units, in which a circulating electric pump, balancing valves for each branch, water meters, thermostat, air outlets are installed, some models are equipped with pressure control devices. Many modifications do not have a built-in bypass, which is usually not installed in two-pipe systems and is considered an unnecessary part in them.But some models have this element, another role of which is to compensate for excess pressure in the underfloor heating pipeline, when it rises, part of the flow enters the return line if its collector is located below the direct one. At the same time, the element reduces the consequences of hydraulic shocks that occur when the circular electric pump is turned on and off in the underfloor heating line.
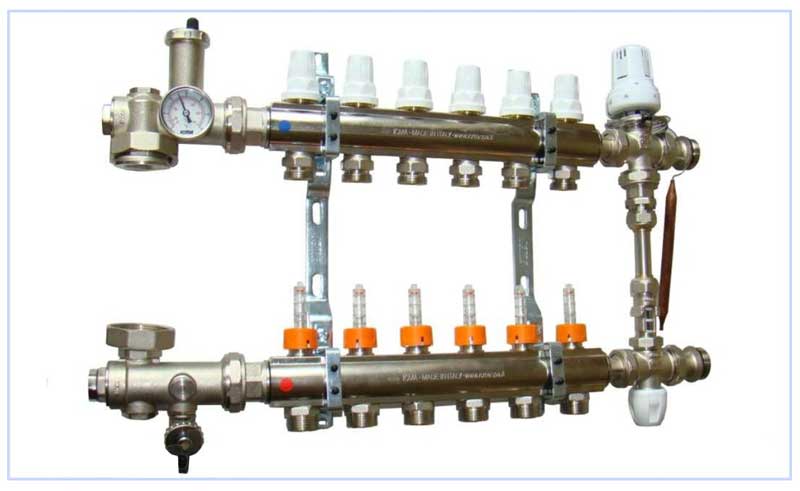


Fig. 13 Manifold with jumper tube
Bypass diameter
Pipe sizing diagram in a system with a bypass on the radiator
So, we already know why a bypass is needed in the heating system and where it is installed. It remains to figure out what diameter it should be. We must consider the options for installing the heating system bypass on the battery and pump separately, since its diameter in each case will be different, which is due to different requirements for it.
The bypass on the pump will be smaller or the same diameter as the main line. How to make a bypass for heating correctly, there is no fundamental difference in this case. After all, it is installed only so that in the event of a pump shutdown, circulation can continue by gravity.
Accordingly, it is impossible to narrow the line itself, while the diameter of the nozzles that depart from the contour is not of key importance. When the pump is stopped, circulation through it will be impossible, therefore, even with an equal diameter with the common line, the bypass will not change the vector of movement of the coolant.
But when installing a bypass in the heating system of a private house on radiators, its diameter is of great importance. It should be one size smaller than the pipes connecting the radiators to the central line. In this case, the outlets to the batteries should also be one size smaller than the main circuit. How it works:
- water flows along the contour and reaches the area where the batteries are installed;
- bumping into a fork, the coolant changes the vector of motion in the direction where there is less resistance;
- part of the coolant continues to move in the same vector.
If the diameter of the nozzles is the same as the bypass, then a small amount of water will get into the batteries, respectively, the temperature of the radiators will drop. If the diameter of the nozzles is less than the diameter of the bypass, then the circulation in the battery will stop altogether.
Reducing the diameter of the pipes in relation to the main line increases the speed of the coolant, which allows it to move more intensively along the radiator. In this case, the water circulates throughout the battery, as a result of which it warms up evenly.
Read more: The principle of the refrigerator: how the device works, the condenser diagram, how the evaporator is tripled in principle
For example, consider a bypass device in a polypropylene heating system. If the diameter of the main line is 32 mm, then the cross-section of the pipes through which water enters the batteries should be 25 mm. The diameter of the bypass in such a scheme, respectively, should be 20 mm. In this case, to the extreme battery, the coolant will pass along the path we need with minimal heat loss. This will make it easier to balance the system.
Bypass in the piping system of a solid fuel heating boiler
The main difference between a solid fuel boiler and a gas boiler is the high combustion temperature of heating materials (charcoal and coal, firewood, peat briquettes, pellets) and the impossibility of adjusting it.
If you heat up solid fuel heating boilers, they reach very high temperatures within a short time, and the interaction of hot air with a cold heat carrier leads to too large a temperature difference. This factor negatively affects the strength characteristics of the materials separating the sources, leading to their accelerated wear - cast iron does not like such temperature fluctuations and can crack, and steel is subject to increased corrosion.In addition, rapid high-temperature heating contributes to the formation of condensate on the surface of the chimney, on which the soot entering with the smoke settles.
The only technically acceptable and competent way out of the situation is to reduce the time period for the interaction of hot air in the boiler with a cold coolant. To solve this problem, a small heating circuit of a solid fuel boiler is created, in which a small amount of liquid circulates. Moving in a closed circle through the bypass jumper, the water quickly warms up, after which it gradually enters the main system through a slightly opening thermostatic valve set at a certain temperature. Hot water mixes with the main heat carrier and gradually heats it up, ensuring a smooth start of the entire system without sudden temperature changes. This technique significantly extends the service life of all equipment, reduces the frequency of preventive maintenance to clean the chimney ducts, and increases the efficiency of the system.
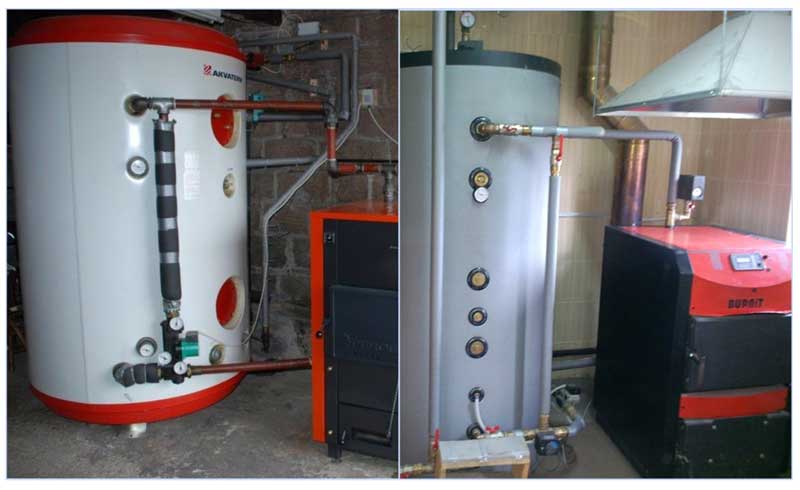


Fig. 14 Bypass in the piping system of a solid fuel boiler
Bypass system: what is this device
A bypass is a bypass pipe that acts as a bulkhead and is equipped with shut-off and adjustable valves. Install the device on a gas pipeline, water supply system, heating system, car, electrical appliances.
In the heating system, a bypass is installed between the forward and return paths near the battery. Such a device allows you to regulate the entry of the coolant into the battery.
During normal circulation of the system, the bulkhead freely passes the fluid flows through itself. If it is necessary to turn off one of the radiators, the element is closed, and the water bypasses a certain section of the system.
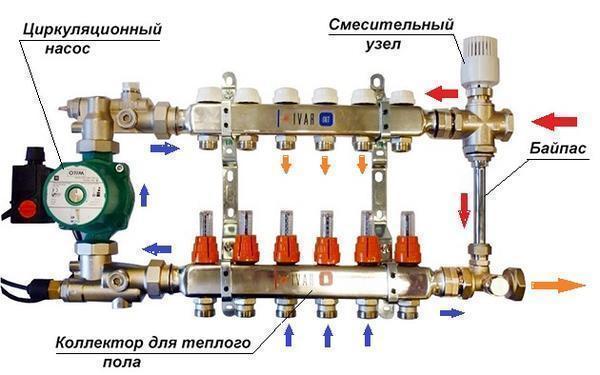

Device advantages:
- Simplifies circuit maintenance;
- Saves energy;
- Prevents airing of pipes;
- Allows you to carry out repairs in case of an accident in the system.
The bypass is produced with mechanical and automatic control. In the first case, the valve is closed and opened manually. The automatic bypass works in autonomous mode. This model is used when installing a circular pump. When the unit is turned on, the bypass valve opens under the pressure of water. When the pump is turned off, it closes automatically. Bypasses are subdivided into radiator and pumping bypasses. Radiators are installed on the way to the battery. They serve to disable contour elements. The second option is used to change the mode or turn off the pump and mount with it.
You can also independently assemble and install a shower stall drain. How to do it? Find out. if you read the article:
Specialist answers to questions
Most often, people who are not well versed in individual heating, the question arises - is a bypass needed in a two-pipe heating system next to radiators? If we consider a one-pipe heating system, a jumper is usually installed in it to ensure the operability of the entire line when one of the heat exchange elements in the circuit is disconnected or malfunctioning, their uniform heating, and the need for a bypass is beyond doubt. In a two-pipe wiring, such problems do not arise by definition, each circuit is connected independently of the others, and a coolant of the same temperature is supplied to everything.
The simplest jumper from the pipe section in the heating line performs many functions in a single-pipe wiring diagram - it maintains constant temperatures on all heat exchangers and the uninterrupted operation of the entire system, ensures high maintainability of the heating elements. Also, a bypass branch pipe can be found in underfloor heating systems and piping of solid fuel heating boilers, where it increases the efficiency and reliability of the equipment.
Application in a two-pipe system
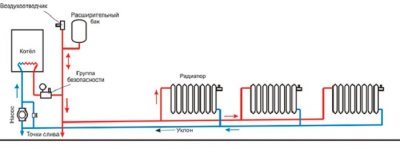

In a two-pipe system, all batteries connected in parallel to the supply and return risers.
Failure of one radiator does not affect the performance of others, therefore the bypass is not used in a two-pipe system: its installation parallel to the heating device is equivalent to a jumper between the supply and return, which worsens circulation and temperature conditions.
Purpose
The bypass returns the coolant used by the heating system to where it came from, thereby stopping the heating of the batteries in the room.
Without a bypass, it is usually impossible to repair radiators connected to the heating system. Also, due to the bypass, the process of cleaning and filling the batteries is simplified several times.
As an example of the irreplaceability of the bypass, we can cite the following situation: if for some reason the electricity supply to the heating system stops, you just need to turn off the tap of the water supply system (near the pump) and open the one on the central pipe. In this case, it will be possible to avoid accidents and save some of the coolant until the energy returns to the system.
There are not only manual, but also automatic bypasses, after the installation of which there is no need for manual control of the system. Some bypasses have a valve that is responsible for supplying the coolant to the system.
When purchasing a bypass, you should not focus on models with a diameter equal to the diameter of the pipes of the heating system installed in the house. The diameter of the bypass tubes should be slightly smaller.
Installing the device
American connection what is it
To simplify the installation of the bypass and ensure safety, it is strongly recommended to use the services of a wizard. Experts will do everything necessary to prevent an accident, both during installation and in the future. Do not forget that the device serves as a kind of home heating controller, which makes it extremely important.
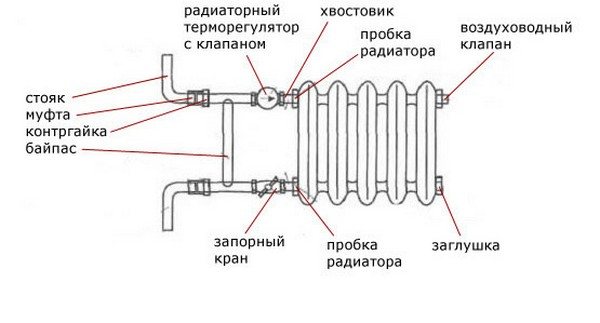

Bypass circuit: constituent elements
The device is installed near the radiator and at a decent distance from the riser. If necessary, an additional tap can be installed on the bypass itself, which guarantees the best circulation of the coolant through the system.
In addition to its original purpose, the bypass, as a rule, can serve as a kind of thermostat due to its ability to regulate hot liquid.
Installation of a device with a circulation pump is as follows:
- the filter is installed first;
- a valve is placed after it;
- then a special circulation pump is installed.
For best results, the bypass must be installed horizontally to avoid air build-up.
It is also worth noting that if this device is also needed on the riser, an additional shut-off valve must be installed.
Prescriptions
In pipe sections where the diameter abruptly goes from large to small, it is worth installing ball valves. These parts are intended so that when they are opened, the clearance of the heating system does not decrease.
This type of valve is a one-piece construction and a ball with a small hole.
In the event of a breakdown of these valves, their repair is impossible - only a complete replacement.
If the ball valves are not used for a long time, they can "stick" to the pipe. To avoid such situations, it is strongly recommended that you scroll through them from time to time.
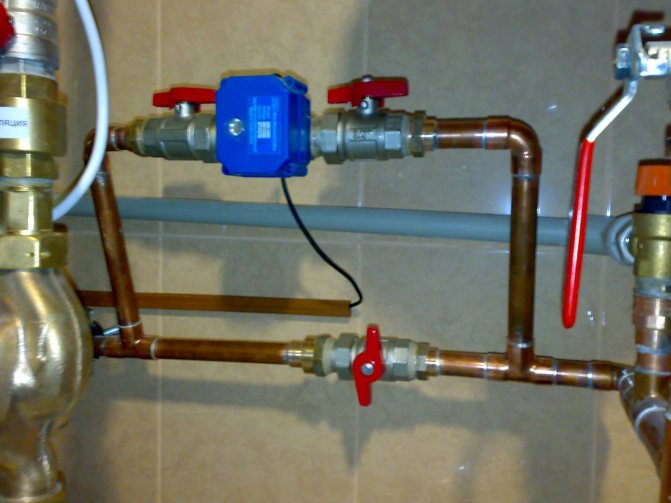


Using a bypass for temperature control